Chapter 03 - Physiology Motility
Showing all 27 results
-
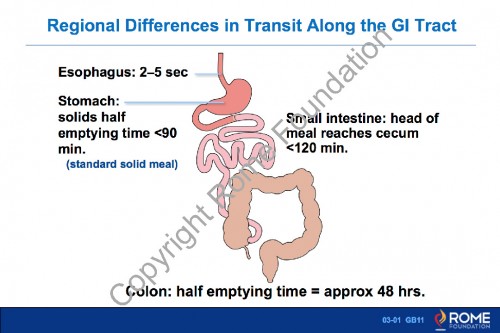
Physiology Motility 01 – Regional Differences in Transit Along the GI Tract
$5.00 -
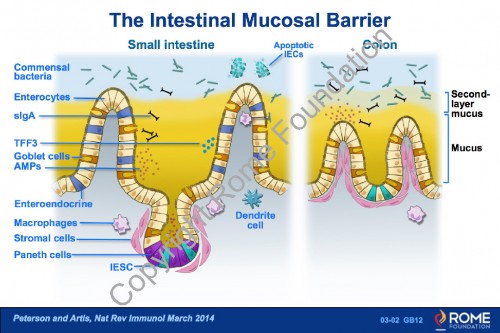
Physiology Motility 02 – The Intestinal Mucosal Barrier
$5.00 -
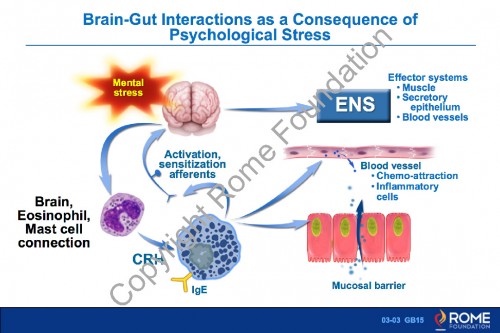
Physiology Motility 03 – Brain-Gut Interactions as a Consequence of Psychological Stress
$5.00 -
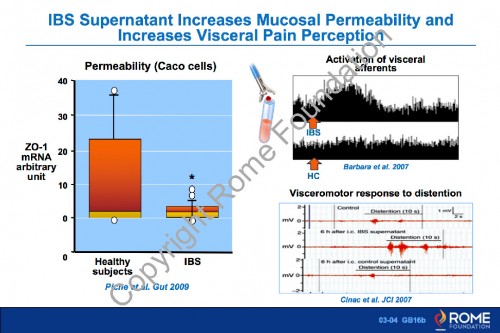
Physiology Motility 04 – IBS Superntant Increases Mucosal Permeability
$5.00 -
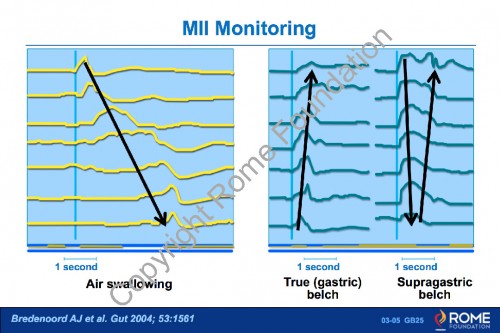
Physiology Motility 05 – MII Monitoring
$5.00 -
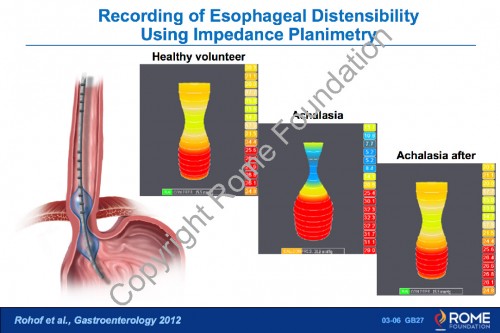
Physiology Motility 06 – Recording of Esophageal Distensibility
$5.00 -
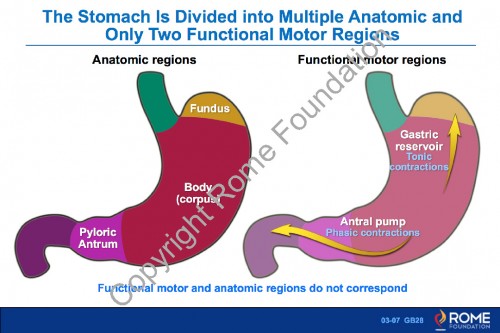
Physiology Motility 07 – The Stomach is Divided
$5.00 -
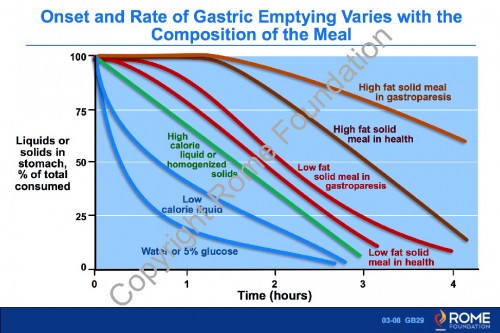
Physiology Motility 08 – Onset and Rate of Gastric Emptying Varies
$5.00 -
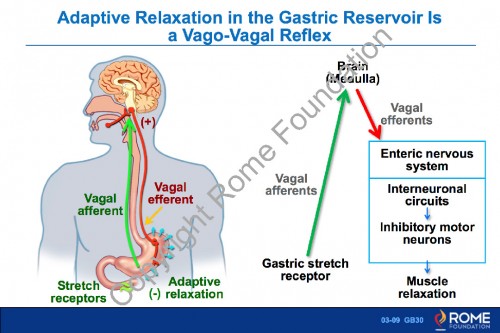
Physiology Motility 09 – Adaptive Relaxation in the Gastric Reservoir
$5.00 -
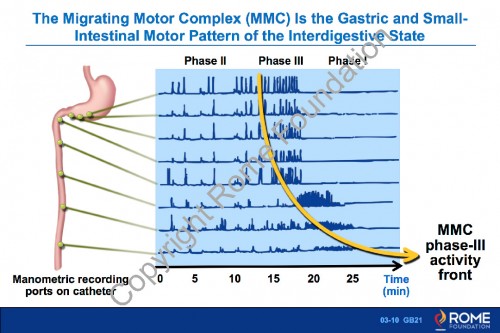
Physiology Motility 10 – The Migrating Motor Complex
$5.00 -

Physiology Motility 11 – High Resolution Phasic Pressure Measurements in the Human Colon
$5.00 -
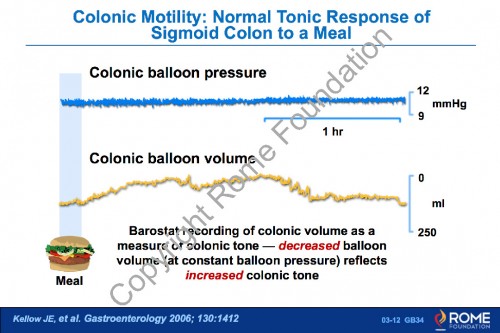
Physiology Motility 12 – Colonic Motility
$5.00 -
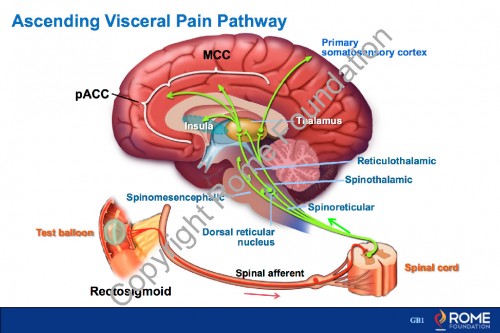
Physiology Motility 13 – Ascending Visceral Pain Pathway
$5.00 -
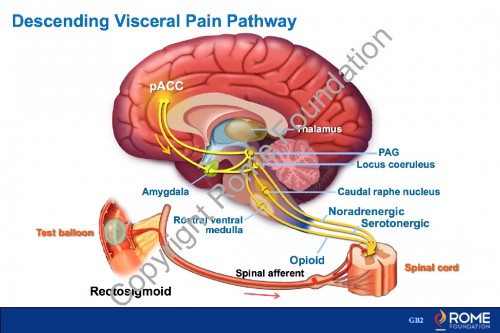
Physiology Motility 14 – Descending Visceral Pain Pathway
$5.00 -
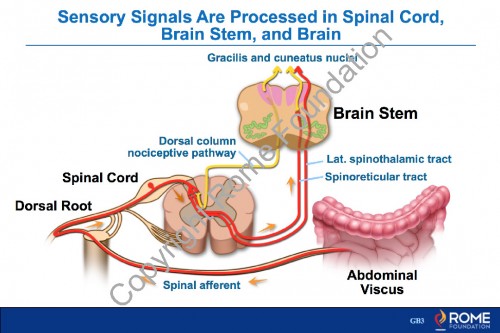
Physiology Motility 15 – Sensory Signals are Processed in Spinal Cord, Brain Stem, and Brain
$5.00 -
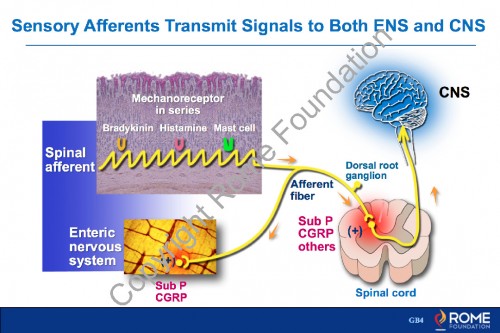
Physiology Motility 16 – Sensory Afferents Transmit Signals to Both ENS and CNS
$5.00 -
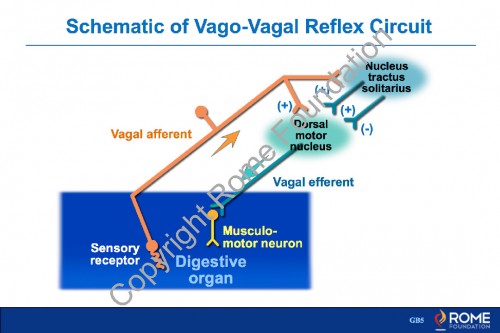
Physiology Motility 17 – Schematic of Vago-Vagal Reflex Circuit
$5.00 -
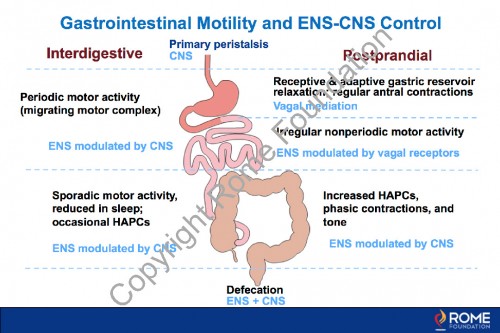
Physiology Motility 18 – Gastrointestinal Motility and ENS-CNS Control
$5.00 -
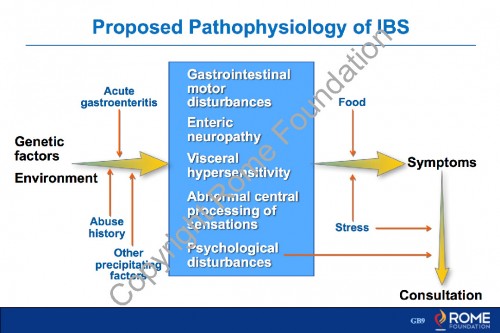
Physiology Motility 19 – Proposed Pathophysiology of IBS
$5.00 -
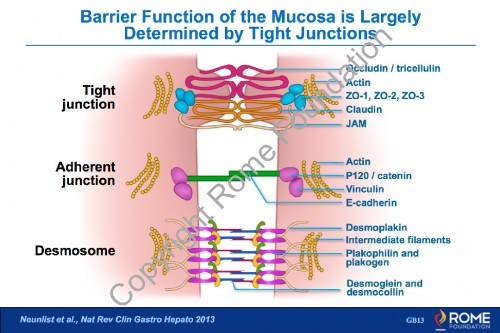
Physiology Motility 20 – Barrier Function of the Mucosa is Largely Determined by Tight Junctions
$5.00 -
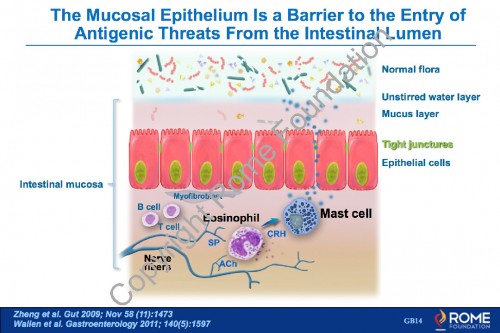
Physiology Motility 21 – The Mucosal Epithelium Is a Barrier to the Entry of Antigenic Threats From the Inestinal Lumen
$5.00 -
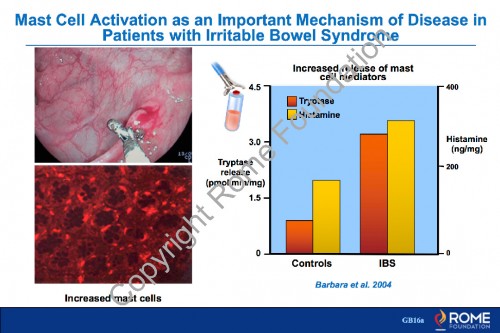
Physiology Motility 22 – Mast Cell Activation as an Important Mechanism of Disease in Patients with IBS
$5.00 -
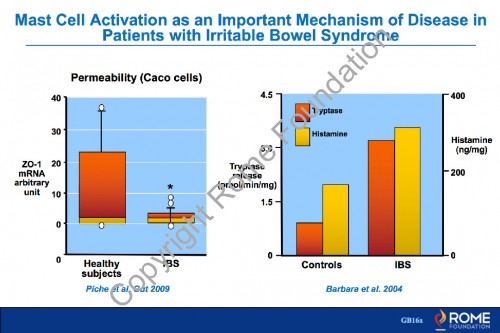
Physiology Motility 23 – Mast Cell Activation as an Important Mechanism of Disease in Patients with IBS
$5.00 -
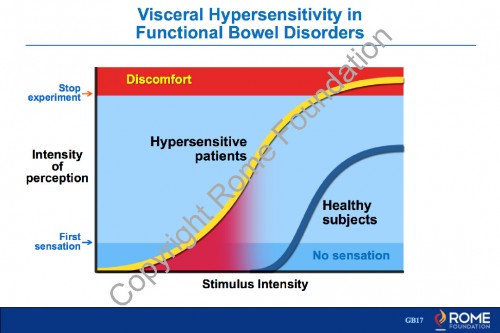
Physiology Motility 24 – Visceral Hypersensitivity in IBS
$5.00 -
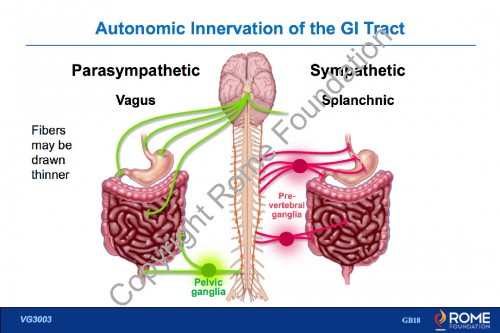
Physiology Motility 25 – Autonomic Innervation of the GI Tract
$5.00 -
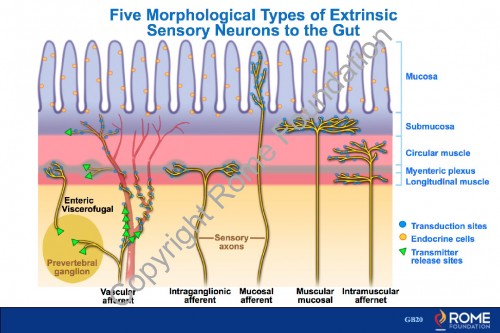
Physiology Motility 26 – Five Morphological Types of Extrinsic Sensory Neurons to the Gut
$5.00 -
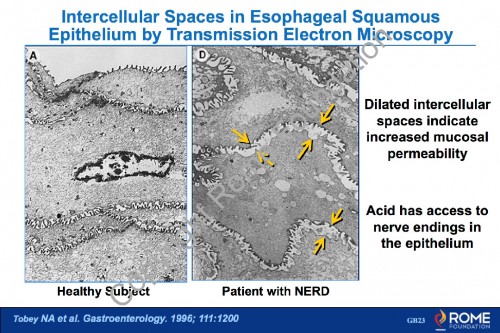
Physiology Motility 27 – Intercellular Spaces in Esophageal Squamous Epithelium by Transmission Electron Microscopy
$5.00
